Curing debilitating genetic diseases is a person of the good troubles of modern-day medication. Throughout the previous 10 years, advancement of CRISPR systems and progress in genetics study brought new hope for individuals and their family members, although the protection of these new techniques is nonetheless of sizeable issue.
Publishing July 1 in the journal Science Innovations, a workforce of biologists at the University of California San Diego that contains postdoctoral scholar Sitara Roy, specialist Annabel Guichard and Professor Ethan Bier describes a new, safer approach that may right genetic flaws in the potential. Their strategy, which would make use of natural DNA mend equipment, provides a basis for novel gene remedy procedures with the likely to cure a significant spectrum of genetic ailments.
In numerous conditions, these suffering from genetic issues carry distinctive mutations in the two copies of genes inherited from their dad and mom. This signifies that normally, a mutation on one particular chromosome will have a functional sequence counterpart on the other chromosome. The scientists employed CRISPR genetic modifying resources to exploit this actuality.
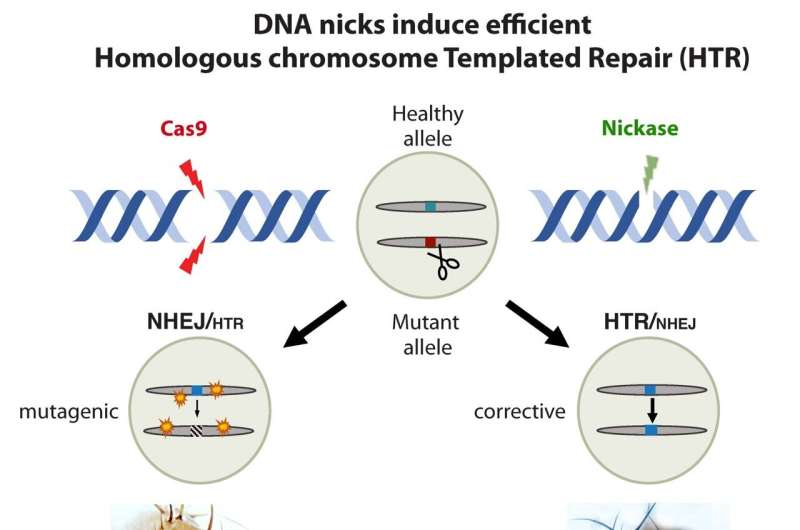
“The nutritious variant can be utilised by the cell’s maintenance equipment to correct the defective mutation following cutting the mutant DNA,” stated Guichard, the senior author of the analyze, “Remarkably, this can be obtained even additional proficiently by a uncomplicated harmless nick.”
Working in fruit flies, the researchers created mutants permitting visualization of this sort of “homologous chromosome-templated maintenance,” or HTR, by the creation of pigments in their eyes. Such mutants in the beginning highlighted entirely white eyes. But when the very same flies expressed CRISPR components (a guidebook RNA plus Cas9), they shown substantial red patches across their eyes, a indicator that the cell’s DNA repair service machinery had succeeded in reversing the mutation working with the useful DNA from the other chromosome.
They then analyzed their new procedure with Cas9 variants acknowledged as “nickases” that targeted just 1 strand of DNA as a substitute of both equally. Astonishingly, the authors located that this kind of nicks also gave rise to significant-amount restoration of red eye color nearly on par with ordinary (non-mutated) nutritious flies. They located a 50-70% repair results fee with the nickase when compared with just 20-30% in dual-strand chopping Cas9, which also generates regular mutations and targets other web pages in the course of the genome (so-termed off-target mutations). “I could not imagine how nicely the nickase worked—it was entirely unanticipated,” claimed Roy, the guide writer of the analyze. The versatility of the new process could serve as a design for correcting genetic mutations in mammals, the scientists pointed out.
“We never know still how this system will translate to human cells and if we can apply it to any gene,” reported Guichard. “Some adjustment could be needed to receive economical HTR for ailment-resulting in mutations carried by human chromosomes.”
The new analysis extends the group’s previous achievements in precision-modifying with “allelic-drives,” which extend on concepts of gene-drives with a guideline RNA that directs the CRISPR technique to slice undesired variants of a gene and change them with a desired edition of the gene.
A critical attribute of the team’s research is that their nickase-dependent method brings about much fewer on- and off-focus on mutations, as is recognized to come about with much more common Cas9-based CRISPR edits. They also say a gradual, continuous shipping of nickase components throughout various times may well establish a lot more helpful than just one-time deliveries.
“An additional noteworthy advantage of this strategy is its simplicity,” mentioned Bier. “It relies on extremely handful of factors and DNA nicks are ‘soft,’ contrary to Cas9, which makes full DNA breaks usually accompanied by mutations.”
“If the frequency of these events could be amplified both by advertising and marketing interhomolog pairing or by optimizing nick-unique maintenance processes, these techniques could be harnessed to appropriate numerous dominant or trans-heterozygous illness-producing mutations,” claimed Roy.
A high-quality-tuned gene editor that minimizes adverse effects
Sitara Roy et al, Cas9/Nickase-induced allelic conversion by homologous chromosome-templated mend in Drosophila somatic cells, Science Advancements (2022). DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.abo0721. www.science.org/doi/10.1126/sciadv.abo0721
University of California – San Diego
Quotation:
‘Soft’ CRISPR may provide a new resolve for genetic problems (2022, July 1)
retrieved 2 July 2022
from https://phys.org/information/2022-07-soft-crispr-genetic-problems.html
This document is subject to copyright. Aside from any truthful working for the goal of personal review or investigation, no
section may possibly be reproduced with out the created authorization. The content material is offered for information reasons only.




