Rampant exploitation of mother nature is a threat to the very well-getting of billions of folks across the globe who depend on wild species for food items, power and money, United Nations biodiversity professionals stated Friday.
From fishing and logging to the use of wild plants in medications and perfumes, societies across the earth use species that have not been tamed or cultivated, with annual world-wide authorized and illegal trade in the hundreds of billions of bucks.
But as humans push alarming biodiversity loss—and local weather modify threatens to accelerate the destruction—the UN’s science advisory panel for biodiversity, IPBES, termed for “transformative adjustments” in our partnership with wild species.
IPBES, which has previously warned that a million species are at possibility of extinction, reported halting overexploitation was “significant to reverse the international development in biodiversity decline” and hailed the essential role of indigenous communities in shielding mother nature.
Its report, composed by dozens of authorities and indigenous advisers and accepted by 139 member states, arrives as the UN steers an intercontinental method to defend character from human destruction in the coming many years.
“The use of wild species is totally crucial for humanity and mother nature,” the IPBES report co-chair Jean-Marc Fromentin advised AFP, incorporating it was a “essential problem for food items safety”.
UN experts estimate “about 40 % of humanity” relies in some way on wild species, he claimed: “It can be a great deal even bigger than you consider.”
Food stuff and fuel
Over-all, 50,000 species are used for meals, strength, medication, materials and other reasons all around the environment, the report claimed, with far more than 10,000 distinct sorts harvested for human usage.
Wild plants, algae and fungi present food items and money for one particular in 5 men and women globally, the report reported, although some 2.4 billion people today depend on wooden for cooking.
IPBES approximated 70 % of the world’s poor rely specifically on wild species and firms joined to them.

But they are not the only ones.
“City dwellers in abundant international locations could not recognize it, but wild vegetation are utilized in medicines or cosmetics, you take in wild fish and there is a fantastic probability that your furniture arrives from wild trees,” explained Fromentin.
Even foraging continues to be an crucial exercise for men and women in North America and Europe, with notably large premiums in Japanese Europe, in accordance to the analysis, which mentioned there is “rising demand from customers for wild meals” for substantial-stop restaurants.
Useful resource ‘robbery’
The international market place for these species is huge small business.
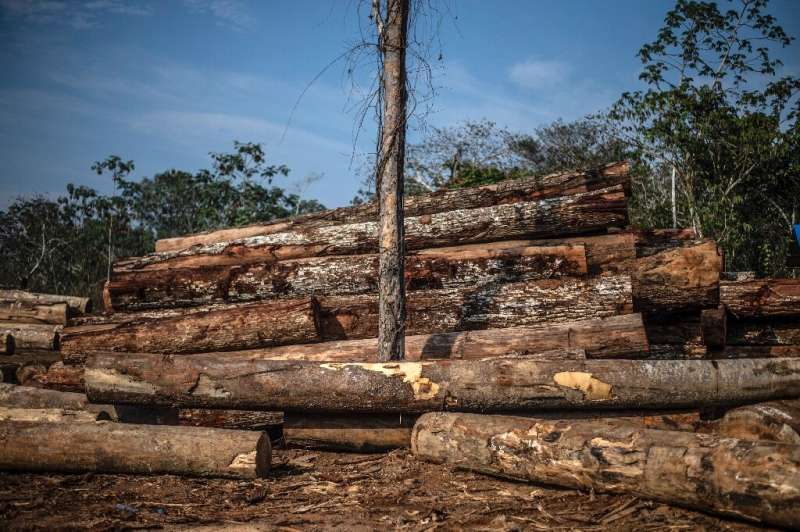
Wild trees account for two thirds of world wide industrial roundwood, while trade in wild plants, algae and fungi is a billion-greenback sector.
But global trade can come to be disconnected from sustainable supply, with surging demand risking species and ecosystems, and the report reported there was an “urgent” have to have for efficient policies that adapt to community requirements.
Just one significant challenge is illicit trade in wild species, believed to be truly worth concerning $69 billion and $199 billion a calendar year, which IPBES stated was the 3rd biggest illegal marketplace right after human trafficking and medicines.
Whilst this mostly targets trees and fish, the report stated even smaller sized-scale trade in rare animals and plants, like orchids, can have devastating consequences.
This trade “robs international locations, indigenous people today and community communities of entry to their very own sources and harmless livelihoods,” explained Inger Andersen, head of the UN Natural environment Method.

Citizen of mother nature
Letting the pure environment thrive is superior enterprise.
Tourism that is based mostly on observing wild species, was a critical explanation that secured regions globally acquired 8 billion visitors and produced $600 billion each individual calendar year in advance of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Meanwhile, fisheries that are properly managed normally have expanding abundance of fish.
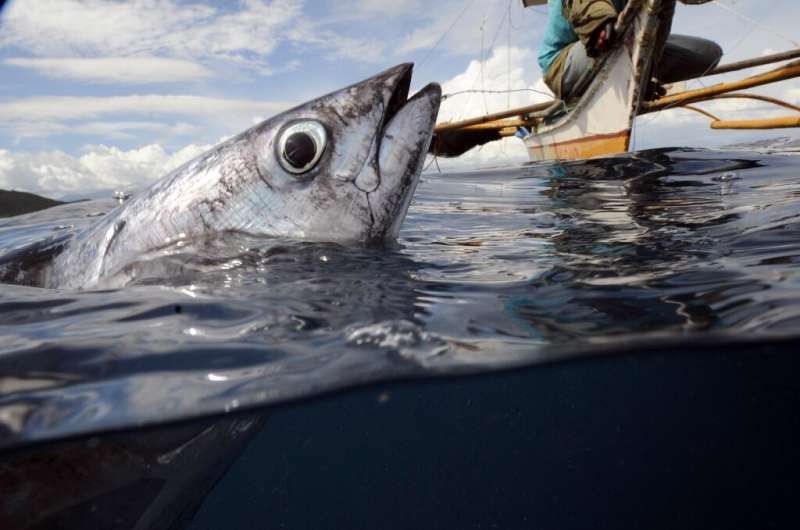
Atlantic bluefin tuna, for illustration, was fished to the brink by an explosion of need for the sashimi current market in the 1980s.
In the beginning “scientific suggestions carried small weight against fisheries lobbies and national pursuits”, IPBES reported, but a new tactic introduced in 2007 has managed to rebuild the population.
In general, overexploitation is the most important menace to wild marine species, it mentioned, as effectively as a key threat to land and freshwater ecosystems.
IPBES termed for policies that assistance the land rights of indigenous people, who steward wide biodiversity-prosperous spots and have generally been underappreciated or pushed off their common homelands in the previous.
The report said much can be learnt from indigenous communities, together with distinctive ways to evaluate species health and fitness, like the total of unwanted fat on a caribou, or the switching flavor of fish.
Co-creator John Donaldson explained the approach of integrating indigenous awareness with much more science-centered exploration experienced been “fairly revelatory”.
The report urged a view of humanity as “a member or a citizen of character between some others”.
It claimed the concept in numerous societies that people are different from and dominant over nature experienced “led to important environmental crises, these as local weather modify and biodiversity decrease”.
Earth missing all targets to help save character, UN warns
© 2022 AFP
Citation:
Billions of individuals depend on wild species for food, gas, cash flow: UN (2022, July 8)
retrieved 11 July 2022
from https://phys.org/information/2022-07-billions-persons-wild-species-food items.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Apart from any reasonable dealing for the function of non-public analyze or analysis, no
aspect could be reproduced without having the composed authorization. The content material is supplied for information reasons only.