Take a look at
The affect of Earth’s geology on existence is straightforward to see, with organisms adapting to environments as various as deserts, mountains, forests, and oceans. The total impact of lifestyle on geology, nonetheless, can be simple to pass up.
A detailed new survey of our planet’s minerals now corrects that omission. Between its conclusions is evidence that about fifty percent of all mineral diversity is the direct or indirect result of dwelling points and their byproducts. It is a discovery that could supply precious insights to scientists piecing jointly Earth’s elaborate geological history—and also to all those hunting for evidence of existence over and above this world.
In a pair of papers revealed on July 1, 2022 in American Mineralogist, researchers Robert Hazen, Shaunna Morrison and their collaborators outline a new taxonomic system for classifying minerals, one particular that locations significance on precisely how minerals type, not just how they appear. In so performing, their technique acknowledges how Earth’s geological growth and the evolution of life influence just about every other.
Their new taxonomy, primarily based on an algorithmic analysis of thousands of scientific papers, recognizes extra than 10,500 diverse varieties of minerals. That’s pretty much two times as several as the about 5,800 mineral “species” in the typical taxonomy of the Intercontinental Mineralogical Affiliation, which focuses strictly on a mineral’s crystalline framework and chemical make-up.
“That’s the classification procedure that’s been utilized for about 200 yrs, and the a person that I grew up with and learned and examined and bought into,” stated Hazen, a mineralogist at the Carnegie Establishment for Science in Washington, D.C. To him, its fixation on mineral composition by yourself has lengthy appeared like a monumental shortcoming.
Back in 2008, he began digging into the literature on each species of acknowledged mineral, wanting for details about how they fashioned. The venture “was a monster to try to tackle,” explained Morrison, who began operating with Hazen at the Carnegie Institution in 2013. The knowledge speedily received murky simply because several mineral species turned out to occur from a number of unique procedures.
Consider, for instance, pyrite crystals (generally recognised as fool’s gold). “Pyrite types in 21 basically different strategies,” Hazen mentioned. Some pyrite crystals type when chloride-prosperous iron deposits heat up deep underground about tens of millions of decades. Other folks type in cold ocean sediments as a byproduct of micro organism that split down natural and organic issue on the seafloor. Still other people are linked with volcanic exercise, groundwater seepage, or coal mines.
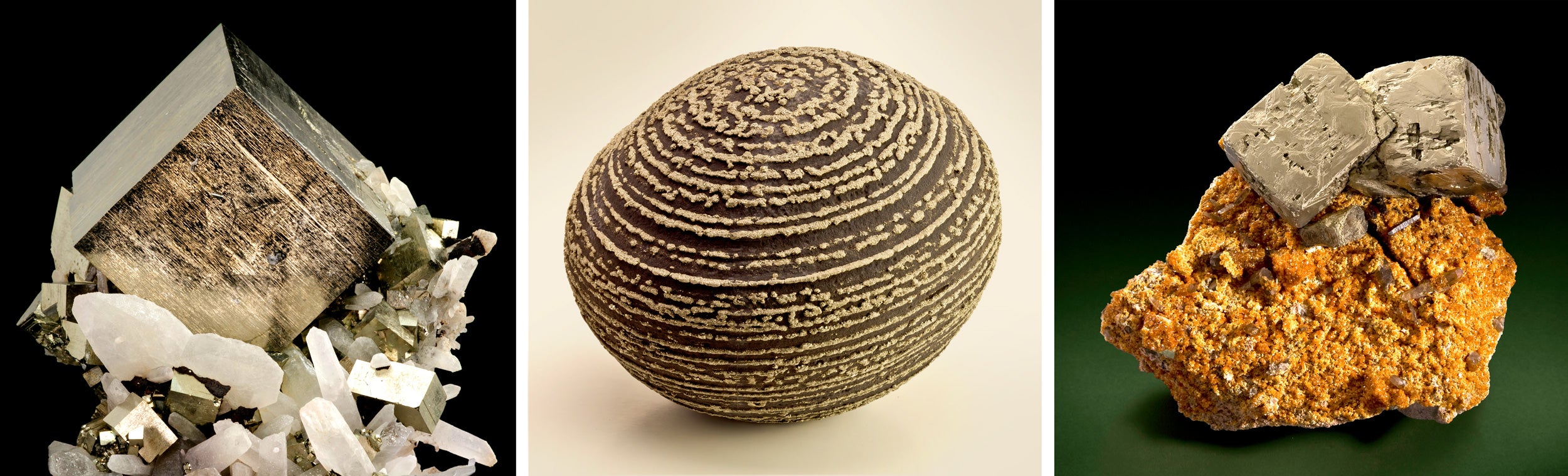

“Each 1 of all those kinds of pyrite is telling us some thing various about our planet, its origin, about daily life, and how it is changed via time,” mentioned Hazen.
For that cause, the new papers classify minerals by “kind,” a term that Hazen and Morrison define as a combination of the mineral species with its mechanism of origin (consider volcanic pyrite vs . microbial pyrite). Working with equipment mastering assessment, they scoured info from thousands of scientific papers and determined 10,556 distinctive mineral sorts.
Morrison and Hazen also determined 57 procedures that independently or in mixture made all regarded minerals. These procedures bundled several kinds of weathering, chemical precipitations, metamorphic transformation inside the mantle, lightning strikes, radiation, oxidation, massive impacts in the course of Earth’s development, and even condensations in interstellar area in advance of the world formed. They verified that the most important solitary issue in mineral variety on Earth is water, which by means of a wide range of chemical and actual physical processes can help to crank out a lot more than 80 % of minerals.
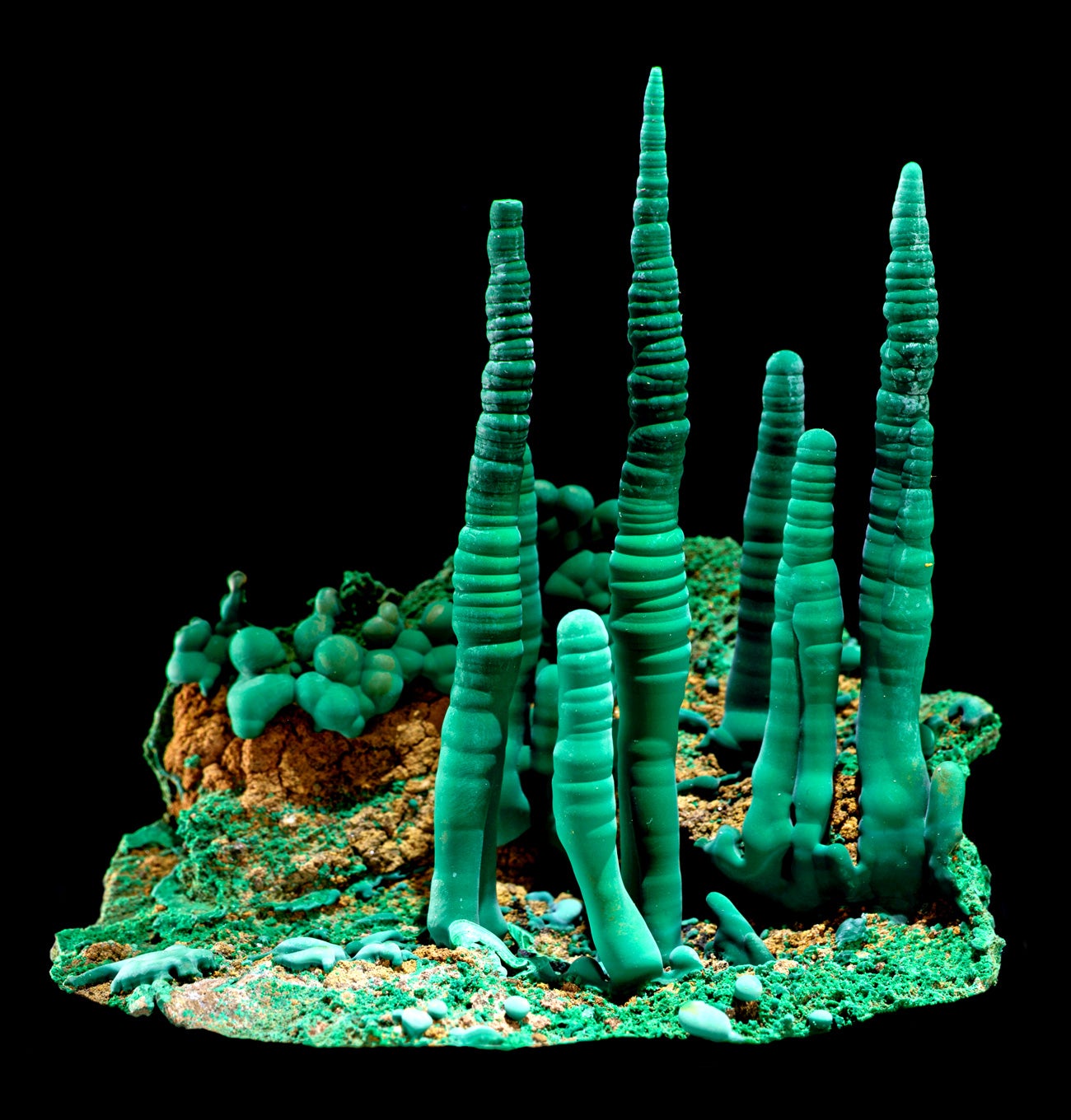

But they also located that everyday living is a vital player: 1-3rd of all mineral sorts variety exclusively as components or byproducts of dwelling things—such as bits of bones, enamel, coral, and kidney stones (which are all prosperous in mineral written content) or feces, wood, microbial mats, and other natural elements that about geologic time can take up aspects from their surroundings and renovate into a thing more like rock. Countless numbers of minerals are shaped by life’s activity in other methods, this sort of as germanium compounds that sort in industrial coal fires. Such as substances developed via interactions with byproducts of life, this sort of as the oxygen manufactured in photosynthesis, life’s fingerprints are on about 50 % of all minerals.
Traditionally, scientists “have artificially drawn a line between what is geochemistry and what is biochemistry,” said Nita Sahai, a biomineralization expert at the College of Akron in Ohio who was not associated in the new analysis. In reality, the boundary amongst animal, vegetable, and mineral is substantially far more fluid. Human bodies, for example, are close to 2 % minerals by body weight, most of it locked away in the calcium phosphate scaffolding that reinforces our enamel and bones.

How deeply the mineralogical is interwoven with the organic could not arrive as a big shock to earth researchers, Sahai claimed, but Morrison and Hazen’s new taxonomy “put a good systematization on it and made it a lot more accessible to a broader local community.”
The new mineral taxonomy will be welcomed by some experts. (“The old 1 sucked,” said Sarah Carmichael, a mineralogy researcher at Appalachian Condition University.) Other individuals, like Carlos Gray Santana, a thinker of science at the College of Utah, are standing by the IMA system, even if it doesn’t acquire the mother nature of mineral evolution into account. “That’s not a challenge,” he said, for the reason that the IMA taxonomy was designed for utilized applications, like chemistry, mining, and engineering, and it however capabilities fantastically in all those parts. “It’s great at serving our realistic needs.”
Yet scientists’ desires are also transforming mainly because of functions like area exploration. 1 implication of Hazen and Morrison’s results is that our watery, dwelling earth is most likely substantially richer in mineral range than other rocky bodies in the photo voltaic procedure. “There are numerous minerals that simply could not form on Mars,” said Hazen. “It doesn’t have penguins pooping on clay minerals, it doesn’t have bats in caves, it does not have cactuses that are decaying or items like that.”
However, Hazen and Morrison hope that their taxonomy may just one working day be used to decode the geologic history of other planets or moons and to research for hints of lifestyle there, past or existing. When examining a Martian crystal, for example, researchers could use the new mineralogical framework to seem at characteristics like grain dimension and framework problems to figure out irrespective of whether it could have been manufactured by an historical microbe relatively than by a dying sea or a meteor strike.
Hazen believes that the new taxonomy may possibly even help with detecting lifestyle on planets about distant stars. Mild from exoplanets detected by the James Webb Room Telescope and other complex devices could be analyzed to figure out the chemical composition of their atmospheres dependent on the measurable oxygen content, the presence or absence of drinking water vapor, relative carbon concentrations and other information, scientists could check out to forecast what sorts of minerals would be possible to sort from light-weight-a long time absent.
Timothy Lyons, a biogeochemist who is aspect of the astrobiology group at College of California, Riverside, thinks that could possibly be pushing the methodology way too significantly, considering the fact that “you’re not going to go to people planets and collect minerals” to validate the success. Even so, he does see Hazen and Morrison’s taxonomy as a potentially crucial source of insights for experiments of extraterrestrial minerals uncovered on our moon and Mars.
“In a definitely zoomed-out, broad-scale way, we are knowing not just our world [but also] our complete photo voltaic process, and perhaps photo voltaic programs past,” Morrison mentioned. “That’s definitely remarkable.”
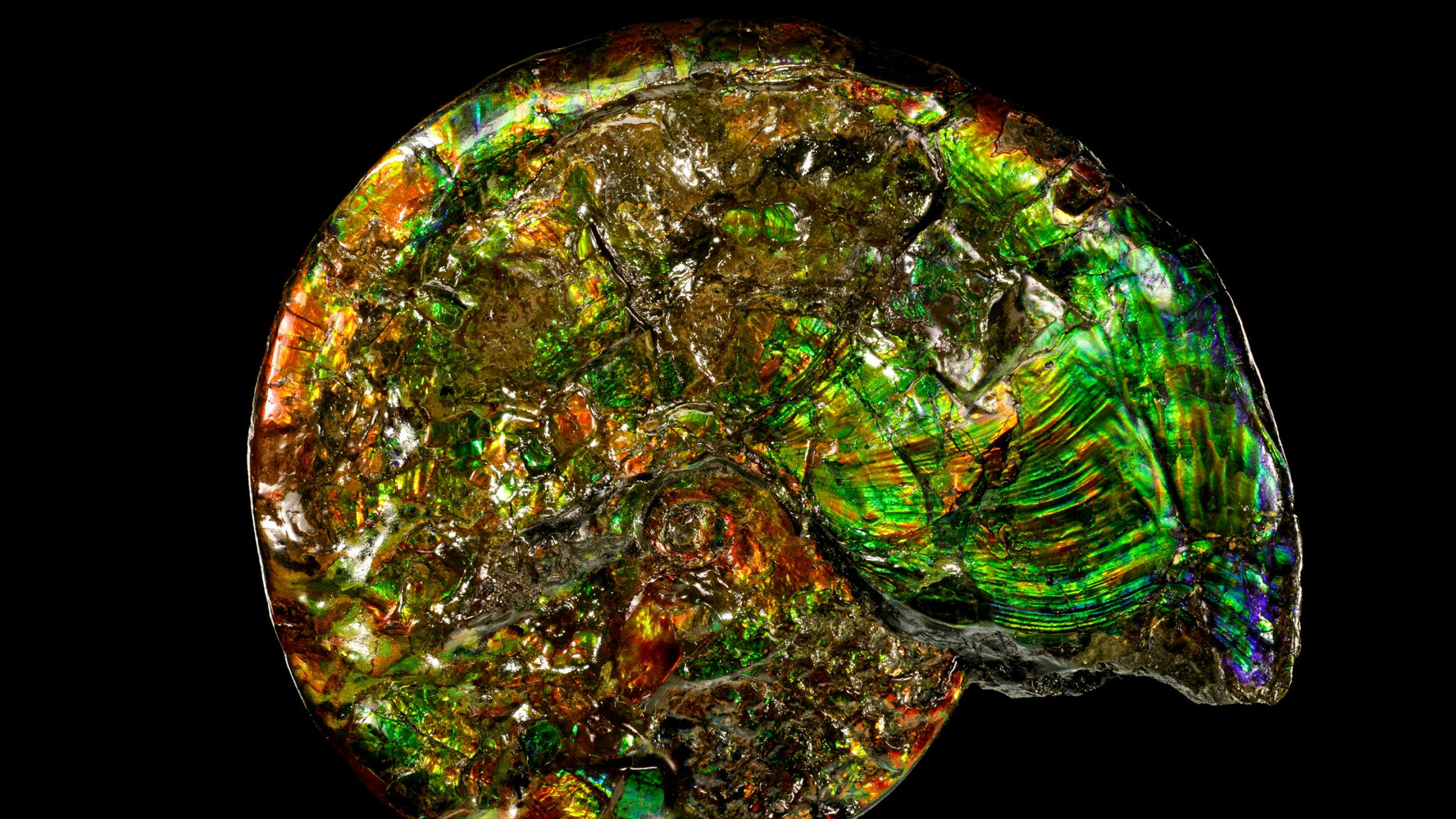
Guide impression: A hundred million decades ago, a sea creature referred to as an ammonite died and its difficult carbonate shell settled into the seabed as a biomineral, aragonite. Over time, the carbonate was steadily replaced with silicate crystals of opal. Image credit: ARKENSTONE / Rob Lavinsky
This report was initially printed on the Quanta Abstractions site.